Pharmaceutical Dryers
 Vacuum Tray Dryer
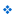
Vacuum Tray Dryer
Vacuum Tray Dryer is used mainly for drying of high grade, temperature and oxygen sensitive products. Vacuum Tray Dryer is highly suitable for drying hygroscopic substances, which are dried to very low residual moisture, content level. Frequently vacuum drying cabinets are the sole possibility for drying lumpy, glutinous products or products of low pomposity.
- Vacuum Tray dryer is the most commonly used batch dryer. They are box-shaped and loaded and unloaded via a door. Inside are several heating plates mounted one above the other on which the product is placed in trays.
- The bottoms of both heating plates and trays should be as smooth as possible to permit optimal heat transfer between plates and product.
- The medium flowing through the heating plates is water, steam or thermal oil.

- The distance between the heating plates is determined primarily by the surface loading and thefoaming of the product.
- To avoid retrograde condensation the cabinet walls are indirectly preheated by the heating plates. Next, the product is introduced and heated at atmospheric pressure. Only after all individual product trays reach the same temperature the cabinet is evacuated and drying can start.
- The preheating phase is very important in order that the drying curve and the foaming of the product is identical throughout the cabinet.
- During the main drying phase the vacuum is in the range of 40 to 80 mbar abs and in the final drying phase vacuums of only few mbar abs are reached.
- Heating temperatures are normally in the range between 800C and 1100C. Depending on product and surface load, drying takes from a few hours to 1 to 2 days.
- For some products the vacuum and temperature profiles are automatically controlled in order to prevent a pass over of the critical product temperature.
- The dimensioning of the vacuum system is an important factor in the design of drying cabinet systems. If for example vigorous foaming of the product is desired, evacuation to the operational vacuum level must take place very quickly.
- Vapours produced during drying are taken out direct, or via a steam jet compressor to a surface condenser in which the vapours condensate. The non-condensable vapours are extracted by the vacuum system.
- On completion of the drying, the product can be cooled by circulating of cooling water through the heating plates.
- Often vacuum drying cabinets are supplied to new, small production operations in newly opened markets. Following successful development of the market, it could be worthwhile to replace the cabinets through continuous vacuum belt type dryers.
 Spray Dryer
Spray Dryer
In Spray dryer, the material to be dried is sprayed as a fine mist into a hot-air chamber and falls to the bottom as dry powder. The period of heating is very brief and so nutritional and functional damage are avoided. Dried powder consists of hollow particles of low density; widely applied to many foods and pharmaceuticals.
The period of heating is very brief and so nutritional and functional damage are avoided. Dried powder consists of hollow particles of low density; widely applied to many foods and pharmaceuticals.
Spray Dryers are relatively simple in operation which accept feed in fluid state and convert it into a dried particulate form by spraying the fluid into a hot drying medium.
 Rotary Dryer
Rotary Dryer
Rotary dryers feed material into a tumbling or rotating drum or tumbler. The drum is then heated or heated air is fed into the unit. The internal surface of the drum may have baffles or louvers to channel the hot air or cascade the material.
- In direct heat rotary dryers a continuous feed of wet particulate material is dried by contact with heated air, while being transported along the interior of a rotating cylinder, with the rotating shell acting as the conveying device and stirrer.
- In the counter-current operation dried material is exposed to the hottest air helping to achieve very low moisture content. The hot gases may enter the dryer at very high temperature.
| Pharmaceutical Machinery: Applications | Pharmaceutical Machinery: Standards | Pharmaceutical Machinery: Indian Market |
| Pharmaceutical Machinery: Global Market | Pharmaceutical Machinery: Technology | Sitemap | Contact |